How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision surveying. Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical skill, encompassing pre-flight checks, understanding regulations, and developing proficiency in controlling the aircraft. This guide will equip you with the essential tools and techniques to safely and effectively navigate the skies with your drone, transforming you from a novice to a confident pilot.
We’ll explore everything from pre-flight safety procedures and understanding airspace restrictions to mastering drone controls, utilizing advanced flight modes, and capturing stunning aerial imagery. We’ll also delve into troubleshooting common issues and performing essential maintenance to ensure the longevity of your drone. Whether you’re a complete beginner or seeking to refine your existing skills, this comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step approach to responsible and rewarding drone operation.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe and efficient drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s components, verifying battery levels, and confirming compliance with local regulations. Ignoring this step can lead to accidents and legal issues.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection, How to operate a drone
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection should cover all aspects of the drone’s physical condition and functionality. This includes checking the propellers, motors, camera, GPS, and battery.
| Issue | Severity | Solution | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Damaged Propeller | High | Replace the damaged propeller. | Regularly inspect propellers before each flight. |
| Low Battery | High | Charge the battery fully. | Always check battery level before flight and carry spare batteries. |
| Weak GPS Signal | Medium | Move to an area with a stronger GPS signal. | Fly in open areas with clear sky visibility. |
| Gimbal Malfunction | Medium | Recalibrate the gimbal or contact support. | Avoid sudden movements and impacts. |
Understanding Local Drone Regulations

Operating a drone requires adherence to local regulations and airspace restrictions. These regulations vary by location and often involve registering your drone, obtaining necessary permits, and respecting no-fly zones.
Consequences for non-compliance can range from fines and the confiscation of your drone to legal prosecution, depending on the severity of the violation. For example, flying near airports without authorization can result in significant penalties and even criminal charges.
Drone Safety Briefing for New Operators
A safety briefing should cover emergency procedures, risk mitigation, and responsible drone operation. This includes instructions on how to handle unexpected situations, such as loss of signal, low battery, or sudden wind gusts.
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Never fly near people or obstacles.
- Be aware of weather conditions and avoid flying in strong winds or rain.
- Familiarize yourself with the emergency procedures of your specific drone model.
- Have a plan for retrieving your drone if it crashes or loses signal.
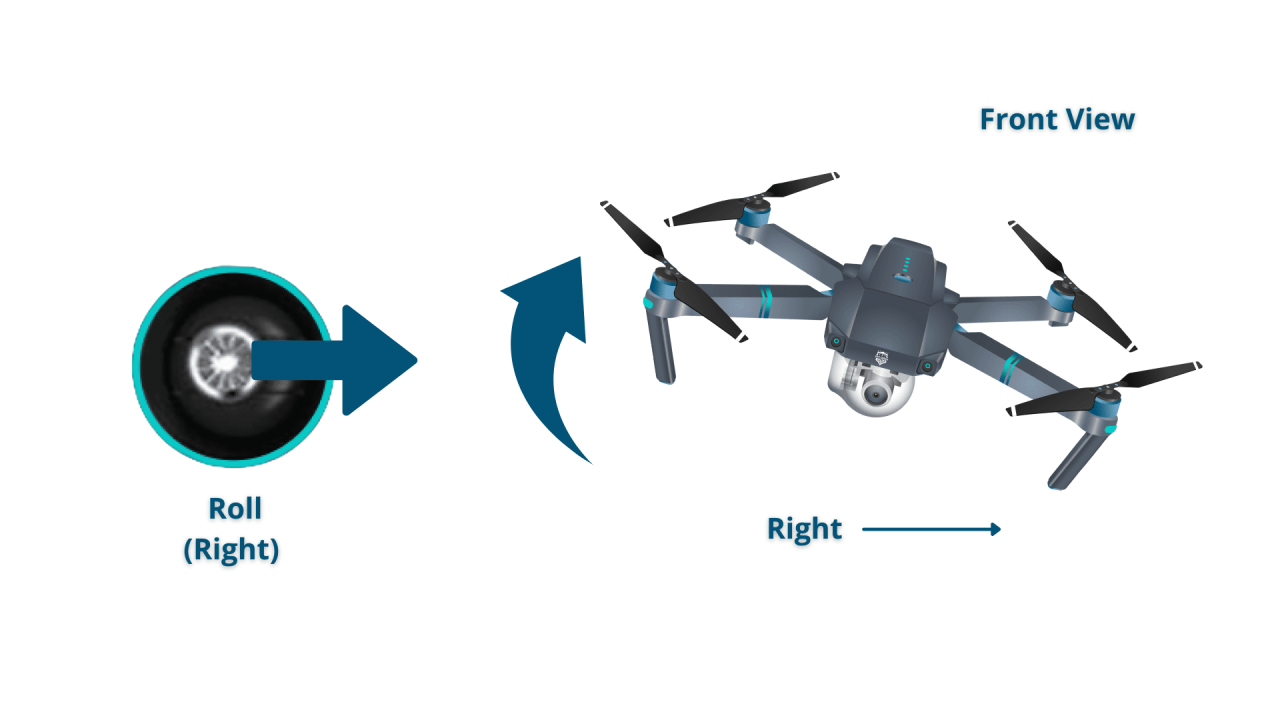
Drone Controls and Operation
Understanding drone controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. Different drones utilize various control methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Types of Drone Controls and Functionalities
Most drones use either joysticks or touchscreen controls. Joysticks offer precise control over the drone’s movement, while touchscreens provide a more intuitive interface, especially for beginners. However, joysticks provide finer control, especially in complex maneuvers.
- Joysticks: Offer precise control over altitude, direction, and camera angle. Ideal for experienced pilots requiring fine control.
- Touchscreen: Provides an intuitive interface, simpler for beginners. May lack the precision of joysticks for complex maneuvers.
Drone Takeoff, Hovering, and Landing Techniques

Smooth and safe takeoff, hovering, and landing are essential for safe drone operation. These techniques should be practiced in a controlled environment before attempting more complex maneuvers.
- Takeoff: Gently increase throttle until the drone lifts off vertically.
- Hovering: Maintain a steady throttle and use the directional controls to keep the drone in place.
- Landing: Slowly decrease the throttle until the drone gently touches down.
Navigating a Drone Using GPS Coordinates and Waypoints
Many drones utilize GPS for navigation, allowing users to program flight paths using waypoints. This enables automated flights, freeing the pilot to focus on camera operation.
- Setting Waypoints: Input GPS coordinates or select points on a map within the drone’s app.
- Programming the Flight Path: Define the sequence of waypoints, setting altitude and speed for each point.
- Initiating the Flight: The drone will autonomously follow the programmed path.
(Screenshots would be included here illustrating each step, showing the waypoint selection interface and the drone following the programmed path. These would visually represent the process.)
Flight Modes and Features
Modern drones offer various flight modes to suit different skill levels and flight scenarios. Understanding these modes is crucial for safe and efficient operation.
Drone Flight Modes and Their Uses
Different flight modes cater to various experience levels and flight situations. Beginner mode limits speed and responsiveness, while sport mode unlocks full capabilities. Choosing the right mode is critical for safety and efficiency.
| Mode Name | Description | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
| Beginner Mode | Limits speed and responsiveness for easier control. | New drone pilots, practicing basic maneuvers. |
| Sport Mode | Unlocks full speed and responsiveness. | Experienced pilots, performing complex maneuvers. |
| Follow Me | Drone automatically follows a designated subject. | Filming moving subjects, tracking individuals. |
| Return to Home (RTH) | Drone automatically returns to its takeoff point. | Emergency situations, low battery. |
Utilizing Advanced Drone Features
Advanced features like obstacle avoidance, return-to-home (RTH), and intelligent flight paths significantly enhance safety and efficiency. These features reduce the risk of accidents and allow for more complex and creative flight operations.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Sensors detect obstacles and automatically adjust the drone’s flight path.
- Return to Home (RTH): The drone automatically returns to its takeoff point in case of signal loss or low battery.
- Intelligent Flight Paths: Pre-programmed flight paths allow for complex maneuvers without manual control.
Camera Operation and Image Capture
The camera is a key feature of most drones, allowing for stunning aerial photography and videography. Mastering camera settings and techniques is crucial for capturing high-quality images.
Adjusting Camera Settings for Optimal Image Quality
Understanding camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture is crucial for capturing high-quality images in various lighting conditions. Adjusting these settings allows you to control brightness, sharpness, and depth of field.
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity to light. Higher ISO values are better in low light but can introduce noise.
- Shutter Speed: Controls the length of time the sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the lens. A wider aperture (smaller f-number) creates a shallow depth of field, blurring the background.
Capturing Various Types of Aerial Shots
Different shot types, such as aerial photos, videos, and panoramas, require specific techniques to achieve optimal results. Mastering these techniques allows for creative and visually appealing content.
- Aerial Photos: Use a fast shutter speed to freeze motion and avoid blurring.
- Videos: Maintain a steady camera angle and smooth movements for professional-looking footage.
- Panoramas: Use the drone’s automated panorama function or manually stitch multiple photos together.
Achieving Specific Camera Movements
Precise camera movements are key for capturing dynamic and engaging visuals. This involves using the drone’s controls to smoothly pan, tilt, and track subjects.
- Smooth Panning: Slowly rotate the camera horizontally to follow a moving subject or capture a wide landscape.
- Tracking Subjects: Use the drone’s follow-me mode or manually control the drone to keep a subject in the frame.
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance: How To Operate A Drone
Post-flight procedures are essential for maintaining the drone’s longevity and ensuring its readiness for future flights. This involves proper battery care, data transfer, and storage.
Post-Flight Checklist
A comprehensive post-flight checklist ensures the drone is properly cared for and ready for the next flight. This includes checking the battery levels, transferring flight data, and cleaning the drone.
- Battery Care: Store batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight.
- Data Transfer: Download flight logs and media files to a computer or storage device.
- Drone Storage: Store the drone in a protective case or bag to prevent damage.
Drone Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular maintenance and cleaning are essential for prolonging the drone’s lifespan and ensuring its optimal performance. This involves inspecting components, cleaning the propellers and body, and lubricating moving parts.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and a solid understanding of the controls; for a comprehensive guide, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic maneuvers to more advanced techniques. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation comes with experience and consistent learning.
- Inspect Components: Check for any damage to the propellers, motors, camera, or other parts.
- Clean the Drone: Use a soft cloth or brush to remove dirt and debris.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Apply a small amount of lubricant to any moving parts, as needed.
Visual Guide to Cleaning and Storing a Drone
Proper cleaning and storage are essential for preserving the drone’s condition and extending its operational life. The following steps ensure the drone is protected from damage and ready for its next use.
- Step 1: Gently wipe down the drone body with a soft, damp cloth. (Illustration: A close-up of someone gently wiping the drone body.)
- Step 2: Clean the propellers with a soft brush to remove any dirt or debris. (Illustration: Someone carefully brushing the propellers.)
- Step 3: Store the drone in a protective case or bag to shield it from dust and damage. (Illustration: The drone securely stored in a protective case.)
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Understanding common drone malfunctions and how to address them is crucial for maintaining smooth operations. This includes recognizing symptoms and implementing appropriate solutions.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Solutions
Several issues can arise during drone operation, requiring prompt diagnosis and resolution. These range from low battery warnings to GPS signal loss and controller problems.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning the basics is crucial for safe and responsible flying, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This guide covers everything from controlling the drone’s movements to understanding battery life and emergency procedures, ensuring you’re well-prepared before your next flight.
- Low Battery: Land the drone immediately and charge the battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Move to an area with a stronger signal or restart the drone.
- Controller Issues: Check battery levels, re-pair the controller, or replace the batteries.
Dealing with Unexpected Situations During Flight
Unexpected events such as sudden wind gusts or loss of control can occur. Having a plan for these scenarios is crucial for safe drone operation and recovery.
- Sudden Wind Gusts: Gently lower the drone to the ground, avoiding abrupt movements.
- Loss of Control: Engage the Return-to-Home (RTH) function if available.
Troubleshooting Flowchart
A visual flowchart helps operators quickly diagnose and solve common problems. This systematic approach streamlines troubleshooting, ensuring efficient problem resolution.
(A flowchart would be included here, visually guiding the user through a series of troubleshooting steps based on the observed issue and leading to potential solutions. The flowchart would be structured to clearly illustrate the decision-making process involved in diagnosing and resolving common drone problems.)
Successfully operating a drone involves more than just mastering the controls; it’s about understanding the technology, adhering to safety regulations, and appreciating the responsibility that comes with flying unmanned aircraft. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you’ll not only gain the skills to operate your drone safely and effectively but also develop a deeper appreciation for the technology and its potential.
Remember, responsible drone piloting ensures a safe and enjoyable experience for everyone, allowing you to explore the skies and capture breathtaking moments responsibly.
Helpful Answers
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with beginner modes and automated features are available. Look for models with GPS, return-to-home functionality, and obstacle avoidance.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and usage. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes, often less in windy conditions.
What happens if I lose the GPS signal during a flight?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that will attempt to return the drone to its starting point. However, maintaining visual contact is crucial.
Do I need insurance for my drone?
Drone insurance is recommended, especially for commercial use or flights in populated areas. It protects you from liability in case of accidents or damage.